Device: Softbank Pepper
Device Type: Humanoid Robot
Firmware: NAOqi System 2.5.5

From the website’s product description:
Pepper is an autonomous talking humanoid robot who perceives emotions, and adapts his behavior to the mood of the humans around him. Pepper can identify joy, sadness, anger or surprise and respond appropriately, making his interactions with humans incredibly natural and intuitive.
Purpose:
Analyze firmware image and extract data in order to search for bugs and vulnerabilities.
Link to download firmware: https://developer.softbankrobotics.com/us-en/downloads/pepper
Download the firmware from the Universal Robots website:
https://developer.softbankrobotics.com/us-en/downloads/pepper
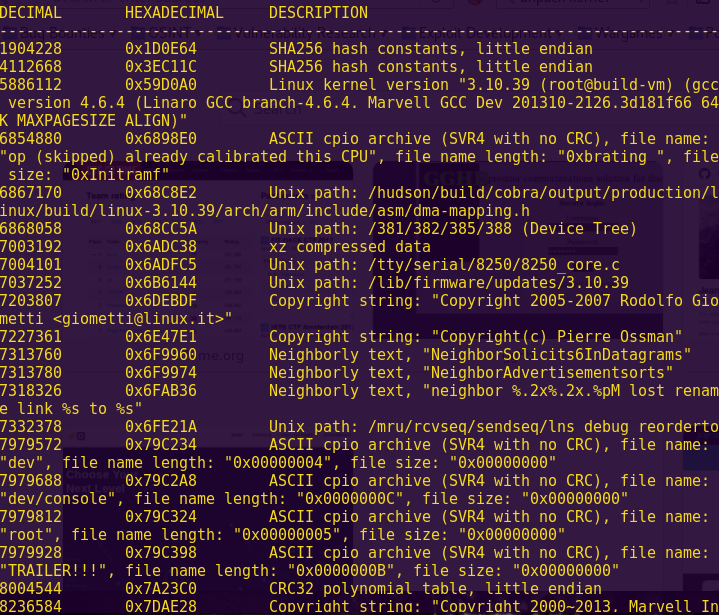
Running the commands “strings” and “hexdump” to extract data:
strings -n 10 pepper-x86-2.5.5.5_2016-11-28.opn > strings.out
hexdump -C pepper-x86-2.5.5.5_2016-11-28.opn > hex.out
Analyzing the strings.out file:

Note we are dealing with a Linux Gentoo-based OS.
Screenshot taken for the lulz, “chest-harakiri”.
About NAOqi OS:
The NAOqi OS documentation can be found here: http://doc.aldebaran.com/2-1/dev/tools/opennao.html
Note that the default passwords are:
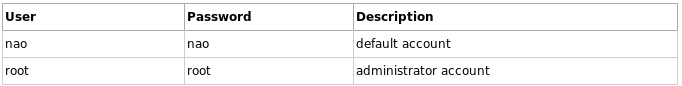
This is important because, unfortunately, as with other IoT devices, most users don’t change the default password.
NAOqi OS is currently used for both the Pepper and NAO robots.
The robot can be connected to via a web browser, SSH, and FTP. Gotta pwn them all!

In the wild:
Softbank sells Pepper for personal use and for business. In fact, some airports, banks, and stores are already using Pepper and report increases in sales.

Source: JapanTimes
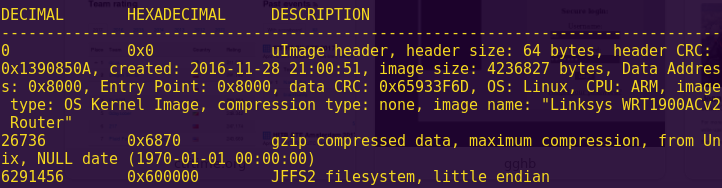
Running “binwalk” to further analyze the image:
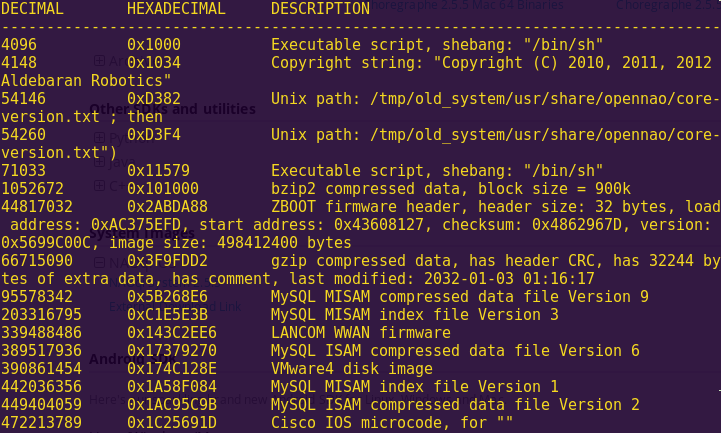
We get information about the bootloader, and the use of other services such as MySQL and Lancom WWAN.
Have fun. 🙂